- Warnings
- Installation
- PATH and .bash_profile
- Homebrew - pyenv
- Uninstall python
- Homebrew
- # install the library using brew brew install libxml2 # go to python site-packages folder (in this case, python 2.7) cd /Library/Python/2.7/site-packages # link all python files from site-packages from brew to current python # (in this case, libxml2 version is 2.9.1) ln -s /usr/local/Cellar/libxml2/2.9.1/lib/python2.7/site-packages/.
- PIL (Python Imaging Library) adds many image processing features to Python. Pillow is a fork of PIL that adds some user-friendly features. CImage.py is a Python module used for image processing. Installing Python, PIL/Pillow, and cImage.py Windows. Install Python 2.7.8 (64-bit — this is important).
It’s easy to install multiple versions of python on a Mac computer using installers from python.org, Homebrew, Conda, or other sources. This could create conflicts if a user wants to run one version of python but bash calls a different version instead.
This is guide will show you how to:
- modify your bash profile to change which version of python is called by bash first.
- use virtual environments to specify a version of python that will run a project.
- uninstall specific versions of python.
Mac OS needs python
Reinstall python and python3 via homebrew. At no time did I touch the python installation located within the /System folder. Oh, and to be clear. The answer to the original question is. Yes, you can trust the old references, as written! That guidance is still valid.
DO NOT remove any versions of Python found in the following folders:
/usr/binsystem/Library
These versions of Python—which should be Python 2.7—are installed by Apple and used by Mac OS and other software to perform some functions. Deleting Python from these directories will break Mac OS and force you to reinstall it on your computer.
Other projects may need specific versions of python
You may have a python project or you may use python packages that require particular versions of Python. Uninstalling those versions would prevent those projects or packages from working until that version of python is reinstalled. For example, Python 3 is a dependency of Numpy; if you uninstalled Python 3, then Numpy wouldn’t work until you reinstalled Python 3.
Three common methods of installing python can be found here:
python.org
The python.org (python.org) installer can be found here.
Homebrew
First install Homebrew. The instructions are here, or enter the following command:
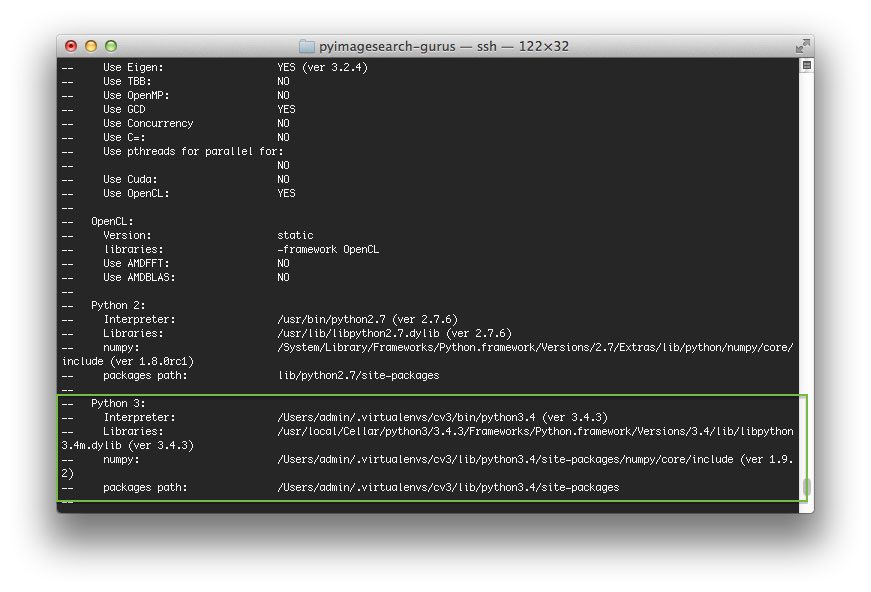
To install Python 3:
To install Python 2:
Anaconda
Anaconda is generally used for scientific and machine learning applications.
For Ananconda follow installation instructions here.
Miniconda is a stripped down version of Anaconda.
For Miniconda follow installation instructions here.
PATH
The path is a list of directories that your shell will look through when you execute a command. You can display the path on your computer using the echo $PATH command:
The directories above are separated by a colon, this is what they look like displayed in sequence:
- /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.7/bin
- /Users/username/anaconda3/bin
- /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7/bin
- /Users/username/miniconda2/bin
- /Users/username/miniconda3/bin
- /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/bin
- /usr/local/bin
- /usr/bin
- /bin
- /usr/sbin
- /sbin
- /usr/texbin
- /opt/X11/bin
- /usr/X11/bin
- /usr/local/git/bin
When you ask your shell to run a particular command or run an interpreter, python for example, the shell looks through the different directories listed in the PATH in order they’re presented above. When the shell finds that command, it stops and calls it even if there is another version of the same command, with the same name, further down in the list.
.bash_profile
The bash profile is a set of instructions that are run by the shell when the user logs in to bash. You can add a variety of preferences to the bash profile, including modifications to the PATH. When anaconda, miniconda or other versions of python are installed they automatically add paths to their respective versions of python to the top of the bash profile.
Bash reads the bash profile in sequential order — from top to bottom — and adds those paths to the PATH in the order that they’re read. This means that the last path at the bottom of the bash profile will end up as the first path in the PATH. This means that if you have Python 3.6 installed on your computer, and then decide to add python 3.7, but keep 3.6, the installer will add Python 3.7 to the top of the bash profile but it will end up after python 3.6 in the PATH. Entering python3 in bash will call python 3.6, not 3.7.
If that was confusing compare the order that the python paths are added to my bash profile below to the PATH listed above. You’ll notice that their respective orders are opposite from each other.
Enter the following command to open the bash profile in TextEdit:
My .bash_profile currently looks like this:
If you want to keep all of your installed versions of python, but want bash to open a different version first, just copy and paste it to the bottom of the bash profile. If you don’t want bash to run a particular version of python then delete it from bash profile and uninstall that version by following the instructions further down.
Don’t forget to save the bash profile before closing TextEdit. You also have to reload the bash profile in bash before any changes take effect. Just enter one of the following commands:
source ~/.bash_profile. ~/.bash_profile
Pyenv is a Homebrew package that allows a user to install multiple versions of python in Homebrew and specify which version of python they’d like to run.
Install pyenv:
Install different versions of python:
Show which versions of python are installed:
The asterisk indicates that the system version of python is active, but 3.5.0 and 3.6.0 are also installed.
Pyenv Local
Create a folder called PythonLocalProject, then display the version of python called by bash by entering python -V:
Now enter:
This creates a .python-version file which tells pyenv which version of python to run in that directory.
Entering ls -la shows us that file:
Now enter pyenv versions:
And running this command shows which version of python is called by pyenv:
To change pyenv to the system version of version 3.6.0 enter:
This procedure is fine, you can set a version of python to run in a particular folder. But what if you want to use pyenv to set a global version of python.
Pyenv Global
Pyenv gives these instructions when you enter pyenv init in bash:
Open the bash profile:
open ~/.bash_profile
Add this text to the bottom of the file:
eval '$(pyenv init -)'
Save the file and then enter:
source ~/.bash_profile
Entering echo $PATH will show that a pyenv shim has been added to the beginnning of the path:
/Users/username/.pyenv/shims:
And which python will return:
/Users/username/.pyenv/shims/python
This means that bash will run the version of python set by pyenv.
Navigate to a folder that doesn’t have a .python-version file and enter:
This shows us that the global version of python is 3.6.0 and it is set by pyenv.
So this shows that bash will run whichever version of python that is set in pyenv.
If you navigate back to the PythonLocalProject folder with the .python-version file and run python -V you will notice that it doesn’t run the global version of python, it runs whichever version was last set with the pyenv local command.
We can use the which command to identify where specific versions of python are located:
This shows some overlap as some versions of python appear in both searches.
The locations of the anaconda and miniconda versions of python are self explanatory, so are the pyenv installs, the python.org installer places python in the /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/ directory. Homebrew installs all packages, including python, in /usr/local/Cellar, then Homebrew adds a symlink to /usr/local/binso that its version of python can be found in the path. Finally, Apple installs python in /usr/bin. Remember, don’t delete that version.
Follow these instructions if you want to remove particular versions of python.
python.org
The python.org installer places all it’s installed files in the following folders:
- The system applications folder,
/Applications /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/usr/local/bin
To delete all versions of python that were installed using the python.org installer, enter these commands in terminal:
To remove particular versions of python, you have to refer to the particular framework. The frameworks are installed in /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework and particular versions are found in /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/X.Y. So for example if you wanted to uninstall only version 3.5 but leave other versions you would enter the following commands in bash:
Homebrew
Install Python Library Mac
To uninstall python that was installed using homebrew you need to identify what versions of python have been installed by Homebrew:
Enter:
Currently brew refers to python3 as python and python 2 is called python@2.
To uninstall both python2 and python3 enter the following:
Homebrew will refuse to uninstall python if it has dependencies, just uninstall python and ignore the dependencies:
Or, add the dependencies to the list of items to be uninstalled:
Troubleshooting
It’s possible to have Homebrew’s Python directory at the beginning of the $PATH but calling python will still start the Apple installed version of Python or some other version. If that’s the case it’s possible that Homebrew’s Python install has become unlinked. This command will unlink and relink Python in Homebrew:
Uninstall Python from Pyenv
To list versions of python installed using pyenv enter:
To uninstall versions of python installed using pyenv enter:
Anaconda
The official removal instructions are found here, but deleting anaconda and miniconda is easy.
Anaconda and miniconda are installed in the users home directory: ~/miniconda2, ~/miniconda3,~/anaconda2, or ~/anaconda3
Depending on which version or versions you have, just enter the following commands:
Anaconda and miniconda also use several invisible files. Delete them by entering this command:
- Python Removal Instructions - towards the bottom of the README file.

And now for something completely different.
Contents
Lesson Goals
This lesson shows you how to download and install Python modules. Thereare many ways to install external modules, but for the purposes of thislesson, we’re going to use a program called pip, easily installable on mac/linux and windows. As of Python 2.7.9 and newer, pip is installed by default. This tutorial will be helpful for anyone using older versions of Python (which are still quite common).
Introducing Modules
One of the great things about using Python is the number of fantasticcode libraries that are widely and easily available that can save you alot of coding, or simply make a particular task (like creating a CSVfile, or scraping a webpage) much easier. When Googling for solutions toproblems, you’ll often find sample code that uses code libraries youhaven’t heard about before. Don’t let these scare you away! Once theselibraries are installed on your computer, you can use them by importingthem at the beginning of your code; you can import as many libraries asyou’d like, such as
For new Python users, it can be a bit intimidating to download andinstall external modules for the first time. There are many ways ofdoing it (thus adding to the confusion); this lesson introduces one ofthe easiest and most common ways of installing python modules.
The goal here is to install software on your computer that canautomatically download and install Python modules for us. We’re going touse a program called pip.
Note: As of Python 3.4, pip will be included in the regular install.There are many reasons why you might not have this version yet, and incase you don’t, these instructions should help.
Mac and Linux instructions
As per the pip documentation, we can download a python script to installpip for us. Using a Mac or Linux, we can install pip via the commandline by using the curl command, which downloads the pip installationperl script.
once you’ve downloaded the get-pip.py file, you need to execute it withthe python interpreter. However, if you try to execute the script withpython like
the script will most likely fail because it won’t have permissions toupdate certain directories on your filesystem that are by default set sothat random scripts cannot change important files and give you viruses.In this case—and in all cases where you need to allow a script that youtrust to write to your system folders—you can use the sudo command(short for “Super User DO”) in front of the python command, like
Windows Instructions
As with the above platforms, the easiest way to install pip is throughthe use of a python program called get-pip.py, which you can downloadhere. When you open this link, you might be scared of the massivejumble of code that awaits you. Please don’t be. Simply use your browserto save this page under its default name, which is get-pip.py. It mightbe a good idea to save this file in your python directory, so you knowwhere to find it.
Once you have saved this file, you need to run it, which can be done intwo ways. If you prefer using your python interpreter, just right-clickon the file get-pip.py and choose “open with” and then choose whateverpython interpreter you care to use.
If you prefer to install pip using the windows command line, navigate towhatever directory you’ve placed python and get-pip.py. For thisexample, we’ll assume this directory is python27, so we’ll use thecommand C:>cd python27. Once you are in this directory, to install pip run thecommand
If you want more information or help with a weird error message, check out the StackOverflowpage that seems to be regularly updated.
Installing Python Modules
Install Python Library Mac
Now that you have pip, it is easy to install python modules since itdoes all the work for you. When you find a module that you want to use,usually the documentation or installation instructions will include thenecessary pip command, such as
Remember, for the same reasons explained above (on Mac or Linux systems, but not Windows), you might need to run pip with sudo, like
Sometimes, especially on Windows, you may find it helpful to use the -m flag (to help python find the pip module), like
Python Library Path
Happy installing!